about Partial Discharge
Partial Discharge Emissions
Bi-Products of PD Activity
-
Light - Sometimes Visible
-
Heat - Infrared • Gases - Nitrous Oxide, etc.
-
Acoustic - Audible and inaudible ultrasonic
-
Electromagnetic - Transmitted UHF or induced TEV or HFCT
-
Chemical - Verdigris - Nitrous Oxide + Moisture = Nitric Acid
PD Testing Methods
Emissions Detected by PMDT's Solutions
Acoustic Emission (AE)
-
Airborne - Ultrasonic Microphone with 40kHz Center Frequency
-
Contact Probe - Broad Bandwidth with 20kHz - 300kHz (Detects PD in Oil or SF6 Gas)
Airborne - Ultrasonic Microphone with 40kHz Center Frequency
Contact Probe - Broad Bandwidth with 20kHz - 300kHz (Detects PD in Oil or SF6 Gas)
Electromagnetic
-
UHF - Ultra High Frequency: 300MHZ - 1.5 GHz
-
HFCT - High Frequency Current Transformer: 500kHz - 50MHz
-
TEV - Transient Earth Voltage: 3MHz - 100MHz
Partial Discharge Types
-
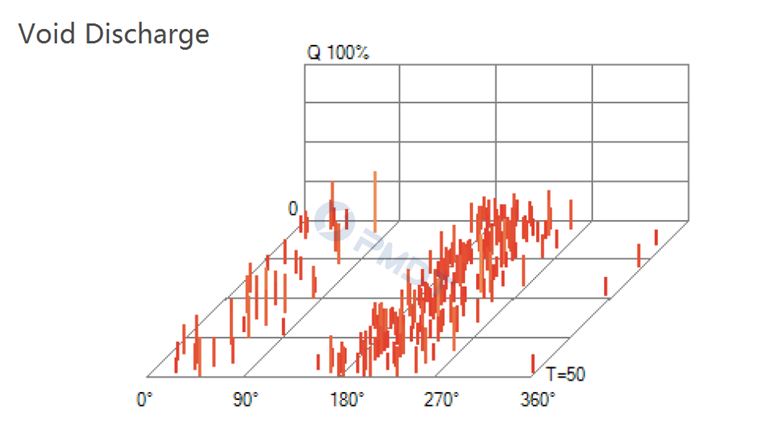
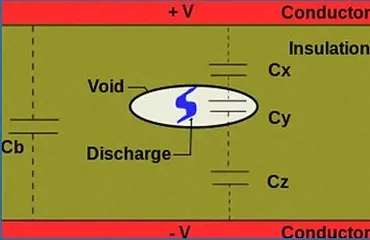
Voids - Gaps in solid insulation or gas bubbles in oil
-
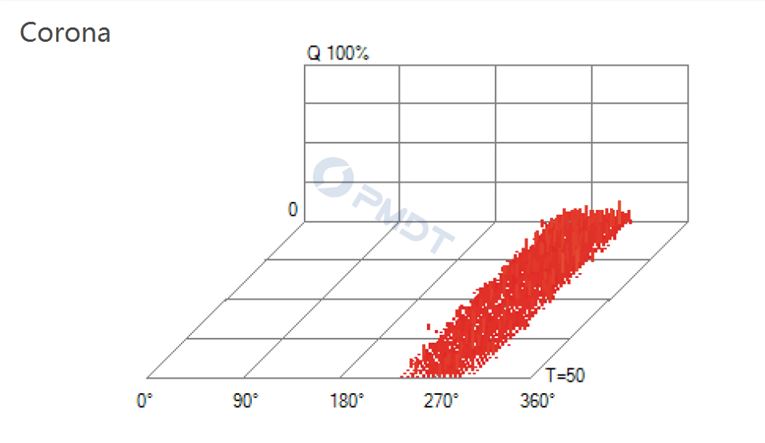
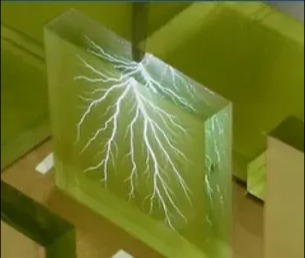
Corona - Discharge to air
-
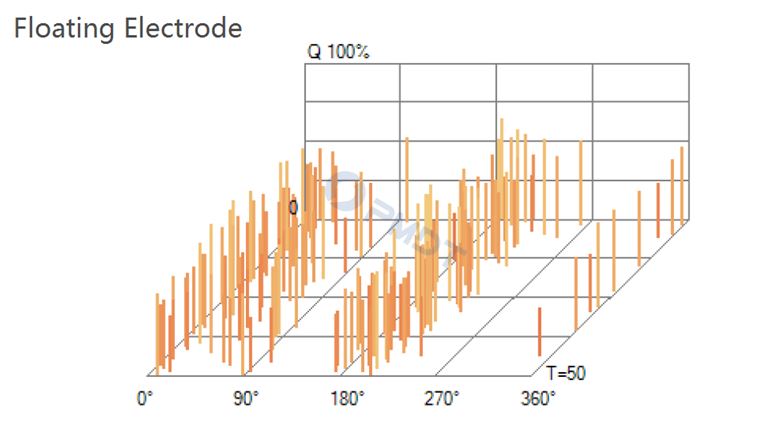
Floating Electrode - Metal to Metal or Metal to insulation defect
-
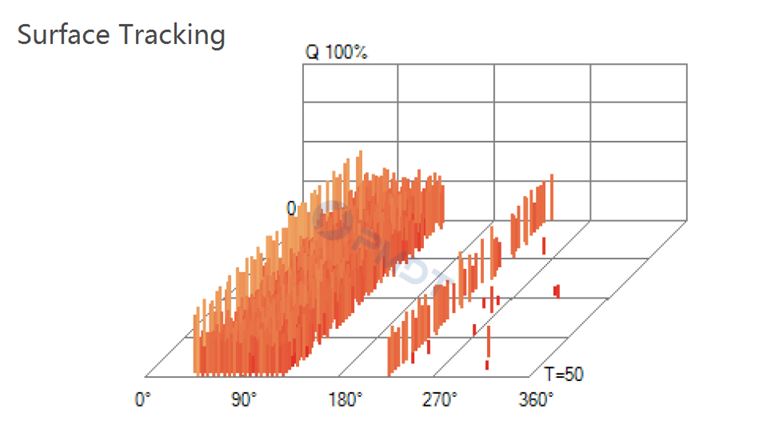
Surface Tracking - Tracking over the outside of insulators
-
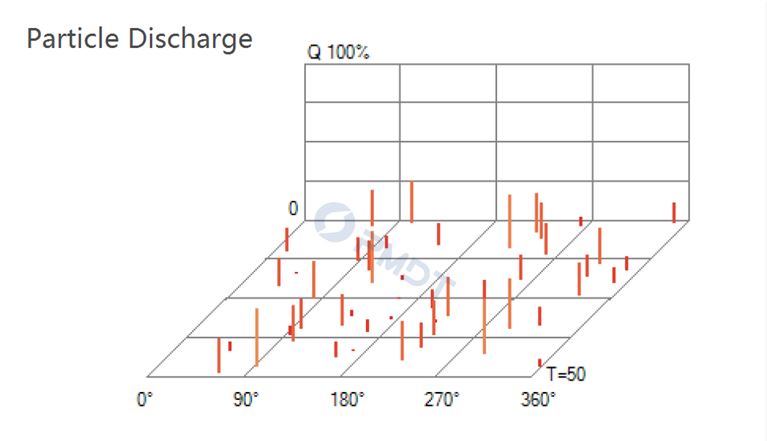
Particle Discharge - Conductive particles contaminate insulation medium
Insulation Failure
Based on IEEE Gold Book Table 36
Component Percentage of Insulation Failure
Transformers 84%
Circuit Breakers 21%
Disconnect Switches 15%
Insulated Switchgear Bus 95%
Bus Duct 90%
Cable 89%
Cable Joints(Splices) 91%
Cable Terminations 87%
Partial Discharge Types
• Void Discharge
This discharge usually occurs due to the manufacturer’s defects in solid insulation. Commonly found in Cables, Bushings, GIS Junction insulation. Highly destructive to insulation. Voids typically continue to grow until failure. If a void PD is discovered, the insulator should be replaced.
• Corona Discharge
Corona is a discharge to air from the sharp surface of a conductor. Corona is typically not a problem besides the sound and the radio frequency emission. Corona signals have many distinct characteristics, allowing it to be easily differentiated from other PD signals.. Corona disturbances do not interfere with other PD measurements.
• Surface Discharge
Also known as "surface tracking". Discharge along the surface of insulation can be very destructive. Usually caused by contamination or weathering of insulator surface. It is different from corona because it tends to track to grounded metal, while corona discharges to air. Corona conditions can evolve into surface PD as they become more severe. This can happen on any MV and HV equipment when strength of insulation breaks down in high humidity environments. or poor maintenance of equipment can lead to this phenomenon. Moisture intrusion is also common cause of surface PD.
• Floating Discharge
Occurs when exposed load carrying conductor is exposed to another conductive surface of different potential not connected to said conductor. Types: Metal to Insulation and Metal to Metal. Usually caused by a manufacturing defect or non-grounded piece of metal within the field. Floating Discharge is the most common type of PD. Often caused by human interaction, such as conductors not positioned properly or foreign or loose object inside of insulation.
• Particle Discharge
Occurs in GIS (SF6 gas) and oil insulated transformers. Caused when conductive particles are left inside system. Allows PD to jump from particle to particle. Purifying and processing the oil or SF6 is recommended.
Vidhyut Engineering delivers reliable electrical testing services and quality industrial electrical solutions - contact us today to discuss your requirements.

Vidhyut Engineering provides complete electrical solutions including industrial products, partial discharge testing services, and technical support. We strive to ensure safe, efficient, and reliable power systems for our clients.
Important links
_____________________________________
Home
About Us
About Partial Discharge
Partial Discharge Service
Contact Us
Services
_____________________________________
Electrical EPC
Online Partial Discharge Testing
Battery Health Analysis
Power System Studies
get in touch
_____________________________________
202, Victoria Heights,
Shree Krishna Park Society,
Himalaya Mall Road,
Bhavnagar-364001, Gujarat, India
+91-9428521618
+91-7043030104
sales@vidhyutengineering.in
info@vidhyutengineering.in